AA Account Metadata For Authentication
ERC-6662 proposes a new IAccountMetadata interface as an extension for ERC-4337 to store authentication data on-chain to support a more user-friendly authentication model. With this new interface, users can store authentication data on-chain through one-time publishing, allowing dApps to proactively fetch it from the chain to support a more flexible and user-friendly authentication model. In the new authentication workflow, users use AA compatible smart contract accounts as their wallet addresses. Authenticator could be anything but holding the private key to sign usersâ operations. Relay is an online service responsible for forwarding requests from dApps to the Authenticator. If the authenticator is online, it can play the role of Relay service and listen to dApps directly. To enable the new authentication workflow, dApp needs to know two things: Where is the authenticator? This is solved by the relayURI field in struct AuthenticationInfo. Users can publish the uri as the account metadata which will be pulled by dApp to do service discovery.
Video
Original
Abstract
This ERC proposes a new IAccountMetadata interface as an extension for ERC-4337 to store authentication data on-chain to support a more user-friendly authentication model.
Motivation
In this proposal, we propose a new IAccountMetadata interface as an extension for ERC-4337 IAccount interface. With this new interface, users can store authentication data on-chain through one-time publishing, allowing dApps to proactively fetch it from the chain to support a more flexible and user-friendly authentication model. This will serve as an alternative to the current authentication model where users need to log in with a wallet every time and push account-related information to dApps by connecting the wallet in advance.
Specification
The key words “MUST”, “MUST NOT”, “REQUIRED”, “SHALL”, “SHALL NOT”, “SHOULD”, “SHOULD NOT”, “RECOMMENDED”, “MAY”, and “OPTIONAL” in this document are to be interpreted as described in RFC 2119.
Authentication Flow
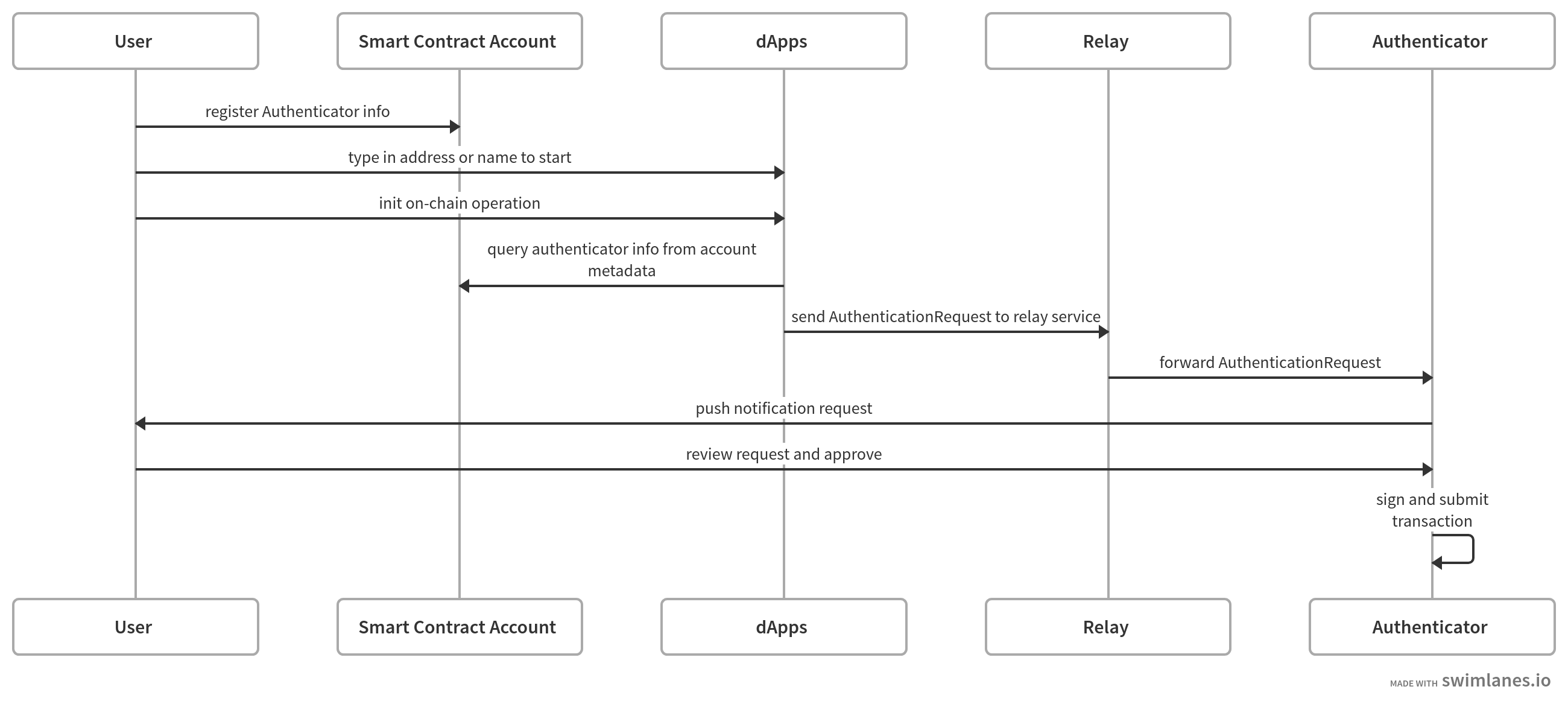
In the new authentication workflow, users use AA compatible smart contract accounts as their wallet addresses. Authenticator could be anything but holding the private key to sign users' operations. For example, it can be an offline authenticator mobile app or an online cloud service. Relay is an online service responsible for forwarding requests from dApps to the Authenticator. If the authenticator is online, it can play the role of Relay service and listen to dApps directly.
Interface
To support the new authentication workflow, this ERC proposes a new IAccountMetadata interface as an extension of IAccount interface defined by ERC-4337.
interface IAccountMetadata {
struct AuthenticatorInfo {
// a list of service URIs to relay message from dApps to authenticators
string[] relayURI;
// a JSON string or URI pointing to a JSON file describing the
// schema of AuthenticationRequest. The URI should follow ERC-4804
// if the schema file is stored on-chain
string schema;
}
function getAuthenticationInfo() external view returns(AuthenticatorInfo[] memory);
}
The relay endpoint should accept an AuthenticationRequest object as input. The format of the AuthenticationRequest object is defined by the schema field at AuthenticationInfo.
Following is a schema example which supports end to end encryption, where we pack all encrypted fields into an encryptedData field. Here we only list basic fields but there may be more fields per schema definition. A special symbol, such as "$e2ee", could be used to indicate the field is encrypted.
{ "title": "AuthenticationRequest", "type": "object", "properties": { "entrypoint": { "type": "string", "description": "the entrypoint contract address", }, "chainId": { "type": "string", "description": "the chain id represented as hex string, e.g. 0x5 for goerli testnet", }, "userOp": { "type": "object", "description": "UserOp struct defined by ERC-4337 without signature", }, "encryptedData": { "type": "string", "description": "contains all encrypted fields" }, } }
Rationale
To enable the new authentication workflow we described above, dApp needs to know two things:
-
Where is the authenticator? This is solved by the relayURI field in struct AuthenticationInfo. Users can publish the uri as the account metadata which will be pulled by dApp to do service discovery.
-
What’s the format of AuthenticationRequest? This is solved by the schema field in struct AuthenticationInfo. The schema defines the structure of the AuthenticationRequest object which is consumed by the authenticator. It can also be used to define extra fields for the relay service to enable flexible access control.
Relay Service Selection
Each authenticator can provide a list of relay services. dApp should pull through the list of relay services in order to find the first workable one. All relay services under each authenticator must follow the same schema.
Signature Aggregation
Multisig authentication could be enabled if multiple AuthenticatorInfos are provided under each smart contract account. Each authenticator can sign and submit signed user operations to bundler independently. These signatures will be aggregated by the Aggregator defined in ERC-4337.
Future Extension
The IAccountMetadata interface could be extended per different requirements. For example, a new alias or avatar field could be defined for profile displaying.
Backwards Compatibility
The new interface is fully backward compatible with ERC-4337.
Security Considerations
End to End Encryption
To protect the user’s privacy and prevent front-running attacks, it's better to keep the data from dApps to authenticators encrypted during transmission. This could be done by adopting the JWE (JSON Web Encryption, RFC-7516) method. Before sending out AuthenticationRequest, a symmetric CEK(Content Encryption Key) is generated to encrypt fields with end to end encryption enabled, then the CEK is encrypted with the signer's public key. dApp will pack the request into a JWE object and send it to the authenticator through the relay service. Relay service has no access to the end to end encrypted data since only the authenticator has the key to decrypt the CEK.
Copyright
Copyright and related rights waived via CC0.
Adopted by projects
Not miss a beat of EIPs' update?
Subscribe EIPs Fun to receive the latest updates of EIPs Good for Buidlers to follow up.
View all